What You Need to Know
- During an incident response engagement, Veloxity discovered a zero-day vulnerability in Atlassian Confluence Server that was exploited to drop the Behinder webshell, which has several capabilities to include the ability to work with Meterpreter and Cobalt Strike. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-26134, is a remote-code execution vulnerability that affects all versions after 1.3.0 of Atlassian’s Confluence Server and Data Center. Atlassian has confirmed that Confluence sites hosted by Atlassian are not vulnerable.
- Atlassian has provided fixes for this vulnerability in the following versions: 7.13.7, 7.14.3, 7.4.17, 7.15.2, 7.16.4, 7.17.4 and 7.18.1. Additionally, for organizations that are unable to upgrade Confluence immediately, Atlassian has provided a temporary workaround for the specific versions of the product, which can be found below in the “Vulnerability Details, Affected Products, and Recommendations” section.
- Observation of this activity may be possible by monitoring for: the creation or addition of .jsp files in the web directory; malicious bash commands like ‘cat /etc/passwd’, ‘cat /etc/shadow’, ‘curl’, and ‘wget’ being run by a web user; suspicious child processes of the web user (specifically bash and python); suspicious inbound web requests with clear or encoded linux commands like “cat”, “wget”, “curl”, “echo”, or “/bin/bash;” and, web logs for URLs containing ${ as this may indicate possible RCE attempts.
- Deepwatch Squads are identifying customers that this vulnerability may impact and evaluating the detection strategy for this exploitation.
During an incident response engagement conducted over Memorial day weekend, Veloxity identified a zero-day vulnerability in Atlassian Confluence Server that was exploited to achieve remote-code execution (RCE). Exploitation included writing JSP webshells to disk.
After discovering the RCE, recreating the exploit, and verification, Veloxity notified Atlassian who confirmed the vulnerability, issued a security advisory, and assigned CVE-2022-26134 to the vulnerability.
Vulnerability Details, Affected Products, and Recommendations
An unauthenticated RCE vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-26134, exists in Atlassian Confluence Server and Data Center products that could allow an unauthenticated threat actor to execute arbitrary code on vulnerable instances.
Atlassian has confirmed that all versions after 1.3.0 of Confluence Server and Data Center are affected. However, Atlassian did note that customers who have their Confluence sites hosted by Atlassian (atlassian.net) are not vulnerable. Atlassian has not identified evidence of exploitation of Atlassian Cloud.
An unauthenticated RCE vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-26134, exists in Atlassian Confluence Server and Data Center products that could allow an unauthenticated threat actor to execute arbitrary code on vulnerable instances.
Atlassian has confirmed that all versions after 1.3.0 of Confluence Server and Data Center are affected. However, Atlassian did note that customers who have their Confluence sites hosted by Atlassian (atlassian.net) are not vulnerable. Atlassian has not identified evidence of exploitation of Atlassian Cloud.
Atlassian has provided fixes for this vulnerability in the following versions:
- 7.13.7
- 7.14.3
- 7.4.17
- 7.15.2
- 7.16.4
- 7.17.4
- 7.18.1
For organizations that are unable to upgrade Confluence immediately, Atlassian has provided a temporary workaround for the following specific versions of the product.
Active Exploitation
During Veloxity’s investigation, it was revealed that once the threat actors successfully exploited CVE-2022-26134, the actors deployed the web server implant Behinder. Behinder web implant has several capabilities to include the ability to work with Meterpreter and Cobalt Strike. Web log analysis revealed that the actor made continuous POST requests (“POST / HTTP/1.1” with status code “200”) to the main index page of the Confluence Server system to communicate with Behinder.
After deploying Behinder, the actors deployed a “custom file upload shell” and the China Chopper webshell. The China Chopper webshell was written to a web directory that was publicly available. Due to the low volume of access to the webshell, Veloxity assessed that it appeared to have been used as a secondary means of access. The China Chopper webshell deployed was the webshell available on tencc’s GitHub repository with no modifications made.
Additionally, the threat actors modified a legitimate Confluence server file named joop.jsp that offers no functionality with the “custom file upload shell.” This webshell was used to allow the actors to upload files to the web server..
Veloxity also discovered that the Confluence web application process was launching bash shells which subsequently spawned a Python process. The Python process then spawned another bash shell.
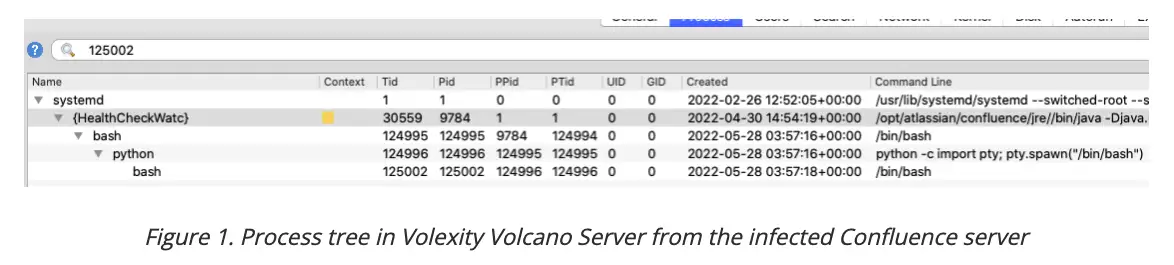
A common command line argument was used to start the Python instance which was used to provide an interactive shell to the threat actor. The interactive shell provided the actor the ability to execute commands as though they were directly logged into the system.
Furthermore, Veloxity’s investigation revealed “that the web server process as well as its child processes created by the exploit are all running as the root (full privileges) user and group.”
Additional activities conducted by the threat actors included:
- System reconnaissance to identify the operating system version.
- Accessed the files “/etc/passwd” and “/etc/shadow.”
- Accessed the Confluence database.
- Dumped the Confluence user tables.
- Attempted to alter web access logs.
- Wrote additional webshells to disk.
Be On the Lookout (BOLO)
It is recommended to audit and monitor logs for the following:
- Creation or addition of .jsp files in the web directory to identify potential webshell installation.
- Malicious bash commands like ‘cat /etc/passwd’, ‘cat /etc/shadow’, ‘curl’, & ‘wget’ being run by web user.
- Suspicious child processes of the web user (specifically bash and python).
- Suspicious inbound web requests with clear or encoded linux commands like “cat”, “wget”, “curl”, “echo”, or “/bin/bash.”
- Web logs for URLs containing ${ as this may indicate possible RCE attempts.
Deepwatch Threat Intel Outlook
Current knowledge gaps prevent the Deepwatch Threat Intel Team from delivering an assessment. These include not knowing if this is a part of a more extensive campaign, the number of victims associated with this campaign, and any commonalities amongst victims. Therefore, out of an abundance of caution, customers that have vulnerable Confluence Server or Data Center instances should update their systems to the latest version as soon as possible or if unable to apply updates implement the temporary workarounds until the systems can be updated.
Sources
https://www.volexity.com/blog/2022/06/02/zero-day-exploitation-of-atlassian-confluence/
https://confluence.atlassian.com/doc/confluence-security-advisory-2022-06-02-1130377146.html?utm_source=alert-email&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=Confluence%20Server%20and%20Data%20Center-advisory-june-2022_EML-13318&jobid=105601969&subid=1541123695
https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2022-26134
Observables
Note:
Observables are properties (such as an IP address, MD5 hash, or the value of a registry key) or measurable events (such as the creation of a registry key or a user) and are not indicators of compromise. The observables listed below are intended to provide contextual information only. Deepwatch evaluates the observables and applies those it deems appropriate to our detections.
Observing sets of these properties (observables) could be an indicator of compromise. For instance, observing an IP address, creation of a user with admin privileges and a registry key could be indicators of compromise and should be investigated further.
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| IP addresses observed communicating with webshells | 154.146.34.145 154.16.105.147 156.146.34.46 156.146.34.52 156.146.34.9 156.146.56.136 198.147.22.148 198.147.22.148 221.178.126.244 45.43.19.91 59.163.248.170 64.64.228.239 66.115.182.102 66.115.182.111 67.149.61.16 98.32.230.38 |
| “Custom file upload shell” | Filename: noop.jsp MD5: f8df4dd46f02dc86d37d46cf4793e036 SHA1: 4c02c3a150de6b70d6fca584c29888202cc1deef |
| China Chopper webshell | .jsp file type MD5: ea18fb65d92e1f0671f23372bacf60e7 SHA1: 80b327ec19c7d14cc10511060ed3a4abffc821af |
Share