EDRKillShifter Targets Endpoint Defenses, Cloud Extortion Exploits .env Files, New DNS Tunneling Backdoor Emerges, Social Engineering Tactics Evolve, 90 Firms Hit by Ransomware, and CISA Updates Exploited List
In our latest Cyber Intelligence Brief, Deepwatch ATI looks at new threats and techniques to deliver actionable intelligence for SecOps organizations.
Each week we look at in-house and industry threat intelligence and provide ATI analysis and perspective to shine a light on a spectrum of cyber threats.
Contents
- New EDRKillShifter Targets Critical Endpoint Defenses
- Cloud Extortion Campaign Leverages Exposed .env Files for Access, Data Theft, and Destruction
- Ongoing Social Engineering Campaign Updates Arsenal
- New DNS Tunneling Backdoor Discovered
- 90 Firms Hit by Ransomware in a Week: Manufacturing, Healthcare, Professional Services Top the List
- CISA Adds Dahua, Linux, Microsoft, Jenkins, and SolarWinds Vulnerabilities to Exploited List
New EDRKillShifter Targets Critical Endpoint Defenses
Ransomware – Malware – EDR Killer – RansomHub – EDRKillShifter – All Industries
The Rundown
Attackers deploying RansomHub ransomware have added a new tool to their arsenal, EDRKillShifter, designed to disable the very systems meant to protect against them.
The emergence of EDRKillShifter is a significant development in the threat landscape. This sophisticated tool is another new threat that targets Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) systems—critical security tools many organizations rely on to protect their endpoints. As ransomware attacks continue to evolve, the discovery of EDRKillShifter underscores the urgent need for enhanced and multi-layered cybersecurity strategies.
Source Material: Sophos
Cloud Extortion Campaign Leverages Exposed .env Files for Access, Data Theft, and Destruction
Data Extortion – Data Theft – Data Destruction – Cloud Environments – Amazon Web Services (AWS) – Exposed Files – Access Keys – All Industries
The Rundown
A recent Palo Alto Networks’ Unit 42 blog post highlights how attackers gained access to AWS environments by using access keys exposed in environmental files, potentially compromising 1,000s of environments. Post-access, the attackers exfiltrated sensitive data, deleted S3 buckets, and demanded a ransom.
This large-scale campaign marks a significant evolution in cloud-based cyber threats, demonstrating how attackers increasingly leverage automation and cloud misconfigurations to orchestrate widespread data breaches. The implications for organizations are severe, extending beyond immediate data loss to long-term risks in operational security and supply chain integrity. The incident underscores the urgent need for enhanced cloud security practices.
Source Material: Palo Alto
Ongoing Social Engineering Campaign Updates Arsenal
Phishing – Spam Emails – Voice Phishing – Remote Monitoring and Management – Cobalt Strike – Ransomware – Black Basta – All Industries
The Rundown
Rapid7 has uncovered an ongoing phishing campaign that has refined its tactics. The campaign, potentially linked to the Black Basta ransomware group, has been active since at least April 2024. The phishing emails flood users’ inboxes and are followed up with convincing phone calls posing as IT support. The phone calls attempt to convince victims to install remote access tools like AnyDesk. Once inside the system, they deploy scripts/malware posing as updates to collect credentials and establish persistence.
The campaign’s evolution in tactics highlights how previous defensive measures can quickly become outdated. In a little over a month, the attackers significantly changed key aspects of the campaign while maintaining the overall intention and objectives. These changes clearly show how static indicators are not foolproof and emphasize organizations’ critical need to employ a defense-in-depth strategy to enhance cyber resilience.
Source Material: Rapid 7 Part 1 & Part 2
New DNS Tunneling Backdoor Discovered
Malware – Vulnerability Exploitation – Backdoor – Msupedge – PHP CVE-2024-4577 – Educational Services
The Rundown
Symantec has discovered a new backdoor named “Msupedge” at a university in Taiwan. The backdoor might represent an escalation in cyber threats due to its use of DNS tunneling to stealthily communicate with its command-and-control servers, blending malicious with legitimate traffic.
The discovery of the Msupedge backdoor is a stark reminder of the evolving sophistication of malware. Its ability to use DNS tunneling to evade detection poses a significant challenge to conventional security measures, potentially leaving critical institutions vulnerable to prolonged and undetected cyber attacks.
This incident, coupled with evidence of the malware’s potential broader distribution, suggests that other institutions may also be at risk, emphasizing the need for heightened vigilance and advanced security measures across sectors.
Source Material: Symantec
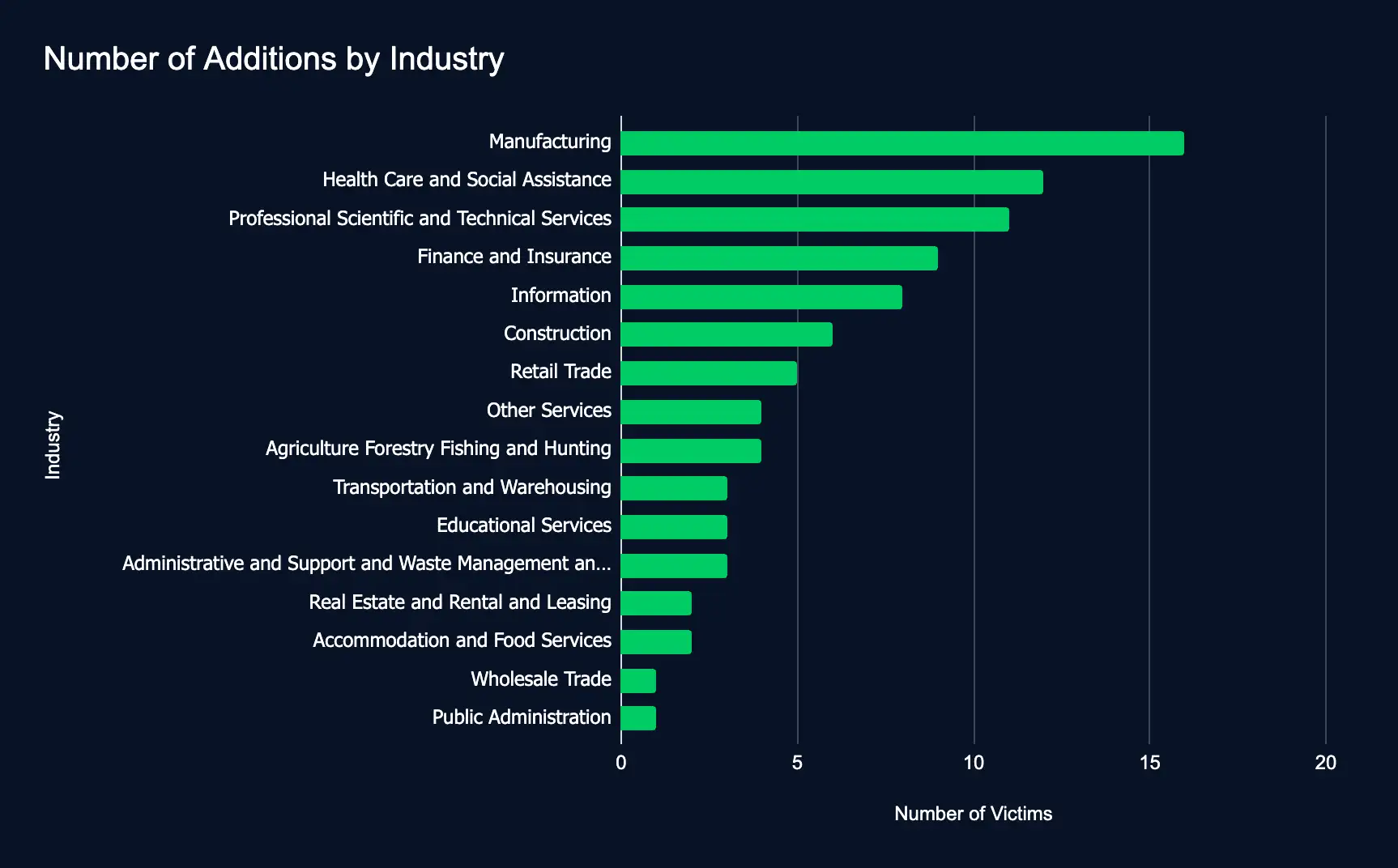
90 Firms Hit by Ransomware in a Week: Manufacturing, Healthcare, Professional Services Top the List
Manufacturing – Health Care and Social Assistance – Professional Scientific and Technical Services – Finance and Insurance – Information
The Rundown
Between August 12 – 18, 2024, 90 organizations were listed on ransomware data leak sites, most of which operate in the manufacturing, healthcare, and professional services sectors.
The consistent targeting of the manufacturing sector and significant increases in attacks on finance and healthcare underscores the growing vulnerability of critical industries. As ransomware groups diversify their targets, the urgency for enhanced cybersecurity measures across various sectors has never been greater.
CISA Adds Dahua, Linux, Microsoft, Jenkins, and SolarWinds Vulnerabilities to Exploited List
Dahua IP Camera CVE-2021-33044 & CVE-2021-33045 – Linux Kernel CVE-2022-0185 – Microsoft Exchange Server CVE-2021-31196 – Jenkins Command Line Interface (CLI) CVE-2024-23897 – SolarWinds Web Help Desk CVE-2024-28986
The Rundown
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has added six new vulnerabilities to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, highlighting the urgency for organizations to patch their systems immediately. These vulnerabilities affect software and hardware from Dahua, Linux, Microsoft, Jenkins, and SolarWinds, posing significant risks across various sectors.
These vulnerabilities have been actively exploited, meaning attackers have used them in attacks, making their inclusion in the KEV catalog a critical alert. Organizations must act swiftly to secure their systems against these threats.
Recommendations
ATI recommends mitigative action occur according to the mitigation “Due Date” recommended by CISA.
Source Material: CISA
What We Mean When We Say
Estimates of Likelihood
We use probabilistic language to reflect the Intel Team’s estimates of the likelihood of developments or events because analytical judgments are not certain. Terms like “probably,” “likely,” “very likely,” and “almost certainly” denote a higher than even chance. The terms “unlikely” and “remote” imply that an event has a lower than even chance of occurring; they do not imply that it will not. Terms like “might” reflect situations where we are unable to assess the likelihood, usually due to a lack of relevant information, which is sketchy or fragmented. Terms like “we can’t dismiss,” “we can’t rule out,” and “we can’t discount” refer to an unlikely, improbable, or distant event with significant consequences.
Confidence in Assessments
Our assessments and projections are based on data that varies in scope, quality, and source. As a result, we assign our assessments high, moderate, or low levels of confidence, as follows:
High confidence indicates that our decisions are based on reliable information and/or that the nature of the problem allows us to make a sound decision. However, a “high confidence” judgment is not a fact or a guarantee, and it still carries the risk of being incorrect.
Moderate confidence denotes that the information is credible and plausible, but not of high enough quality or sufficiently corroborated to warrant a higher level of assurance.
Low confidence indicates that the information’s credibility and/or plausibility are in doubt, that the information is too fragmented or poorly corroborated to make solid analytic inferences, or that we have serious concerns or problems with the sources.

Share