Cyberespionage Uses Open-source Tools, FIN7 Tool AvNeutralizer Sold, SocGholish Delivers AsyncRAT, Serverless Computing Threats, Credit Card Data Theft via Swap Files, ICS Malware Modbus Threat, Ransomware Surge, and 2 New Vulnerabilities
In our latest Cyber Intelligence Brief, Deepwatch ATI looks at new threats and techniques to deliver actionable intelligence for SecOps organizations.
Each week we look at in-house and industry threat intelligence and provide ATI analysis and perspective to shine a light on a spectrum of cyber threats.
Contents
- Cyberespionage Attacks Use Open-source Tools, PoCs to Target Government and Private Sectors’ Internet-facing Appliances
- Former FIN7 Tool AvNeutralizer Now Known to be Sold in Cybercriminal Forums
- SocGholish Delivers AsyncRAT and Legitimate Volunteer Computing Client, BOINC
- Threats to Serverless Computing: What You Need to Know
- Attackers Abuse Swap Files to Steal Credit Card Data and Thwart Cleanup Attempts
- First ICS Malware Using Modbus Poses New Global Threat
- Ransomware Surge: 91 Firms Listed on Data Leak Sites in the Past Week
- IE and Twilio Authy Vulnerabilities Now on Exploited List
Cyberespionage Attacks Use Open-source Tools, PoCs to Target Government and Private Sectors’ Internet-facing Appliances
Cyberespionage – Exploitation of Internet-facing Appliances – CVE-2019-9621 – CVE-2024-3400 – Remote Access Trojans – Penetration Testing Tools – Pantegana – SparkRAT – LESLIELOADER – Cobalt Strike – Manufacturing – Educational Services – Finance and Insurance – Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services – Public Administration – Other Services – Utilities
The Rundown
Recorded Future’s Insikt Group has identified TAG-100, a cluster of suspected cyber-espionage activity. This group targets internet-facing appliances for initial access, using publicly available exploit code and open-source tools for post-exploitation. Their operations impact high-profile government, intergovernmental, and private sector organizations worldwide.
TAG-100’s activity emphasizes the vulnerability of internet-facing appliances, highlighting the need for robust security measures across various sectors. The group’s tactics and use of publicly available tools demonstrate that sophisticated cyber espionage can be carried out with minimal resources, posing a significant threat to global security.
Source Material: Recorded Future (PDF)
Former FIN7 Tool AvNeutralizer Now Known to be Sold in Cybercriminal Forums
Malware – AV Tampering Malware – AvNeutralizer – All Industries
The Rundown
SentinelOne has discovered that FIN7 attackers are now offering the antivirus tampering tool, AvNeutralizer, once exclusive to Black Basta, for sale across multiple cybercriminal forums.
The sale of AvNeutralizer to multiple attackers increases the potential for widespread tampering with security solutions, posing significant threats to organizations’ cybersecurity defenses.
FIN7 is a financially motivated group that has been active since 2013. The group is believed to be based in Russia and primarily focuses on financial fraud and cyberattacks targeting organizations in various sectors.
They gained notoriety for their sophisticated phishing and social engineering tactics, which they use to gain initial access to corporate networks. The group has impersonated various legitimate businesses and developed custom malware and attack tools.
Source Material: SentinelOne
SocGholish Delivers AsyncRAT and Legitimate Volunteer Computing Client, BOINC
Malware – SocGholish – Fake Browser Update – AsyncRAT – BOINC (Berkeley Open Infrastructure Network Computing Client) – All Industries
The Rundown
Beginning on July 4, 2024, Huntress observed fake browser updates that led to the installation of AsyncRAT and a publicly available computer resource donation application known as BOINC (Berkeley Open Infrastructure Network Computing Client). Huntress states that the activity observed overlaps with malware campaigns known as SocGholish/FakeUpdates.
Clients infected with AsyncRAT and/or actively connecting to malicious BOINC servers present a reasonably high risk, as an attacker could execute any number of malicious commands or malware on the host to further escalate privileges or move laterally through a network and compromise an entire domain.
Infections typically begin as a result of a user visiting a compromised website, which results in a fake browser update prompt to the user. Downloading and launching the update executes a Javascript file that executes two distinct infection chains. One chain downloads AsyncRAT and the other downloads the BOINC client.
BOINC is a publicly available application that aids science research. The project aims to facilitate users to donate computer resources for various legitimate science projects that require significant processing power. The BOINC client allows the user’s computer to connect to a remote server that can collect information and send tasks to the host for execution in the background.
Source Material: Huntress
Threats to Serverless Computing: What You Need to Know
Phishing – Malware – Proxying Malicious Traffic – Threat Actor – Cryptomining – Astaroth infostealer – PINEAPPLE – FLUXROOT – All Industries
The Rundown
Serverless computing, while offering scalability and efficiency, faces significant security threats that organizations must address to protect their cloud environments. Google Cloud’s H2 2024 Threat Horizon Report highlights the need to prioritize weak credentials, misconfigurations, and malware delivery defenses.
As businesses increasingly adopt serverless computing, understanding these threats is crucial for organizations to effectively secure their cloud environments, prevent unauthorized access, and protect sensitive data.
Source Material: Google
Attackers Abuse Swap Files to Steal Credit Card Data and Thwart Cleanup Attempts
Credit Card Skimming – Swap File Abuse – Retail Trade – All Industries
The Rundown
Sucuri discovered attackers are now abusing swap files to steal credit card data, allowing the skimmer to persist through multiple cleanup attempts.
Using swap files to steal credit card data significantly escalates cyber threats. This method not only compromises sensitive information but also evades standard malware cleanup efforts, increasing the risk and potential damage from such breaches.
Source Material: Sucuri
First ICS Malware Using Modbus Poses New Global Threat
ICS Malware – FrostyGoop – Modbus – Operational Technology (OT) – All industries employing ICS devices
The Rundown
Dragos discovered a new industrial control systems (ICS) specific malware, dubbed FrostyGoop, in April 2024. It can interact directly with ICS using Modbus, a standard ICS protocol across all industrial sectors and organizations worldwide. It is the first ICS-specific malware that uses Modbus TCP communications to achieve an impact on Operational Technology (OT).
Given the widespread use of Modbus devices globally, FrostyGoop’s broad applicability to ICS networks underscores its significance. This discovery necessitates the development of detections of vulnerabilities and Modbus traffic, attack vectors, and malware targeting Modbus systems.
Source Material: Dragos
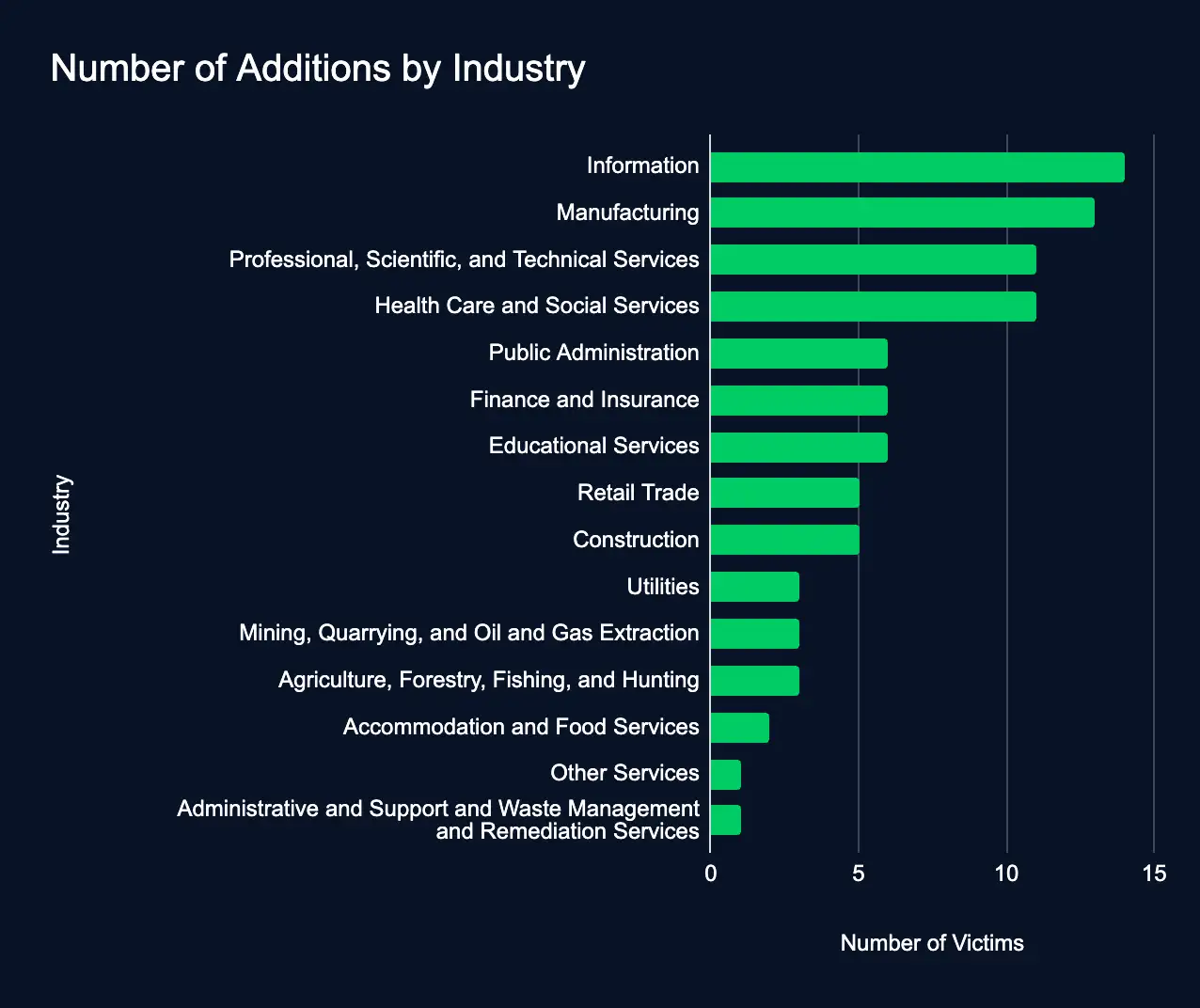
Ransomware Surge: 91 Firms Listed on Data Leak Sites in the Past Week
Information – Manufacturing – Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services – Health Care and Social Services – Public Administration – Finance and Insurance – Educational Services – Retail Trade – Construction
The Rundown
In just one week, 90 organizations across various industries and countries have been listed on ransomware data leak sites, indicating an escalation in cyberattacks.
This surge in ransomware leak site additions, doubling the previous week’s numbers and reversing a trend of declining additions, underscores the growing cyber threat landscape. For organizations, staying vigilant, identifying potential third-party risks, and enhancing security measures are crucial to mitigate these escalating risks.
By the numbers:
IE and Twilio Authy Vulnerabilities Now on Exploited List
Microsoft Internet Explorer CVE-2012-4792 – Twilio Authy CVE-2024-39891
The Rundown
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has added vulnerabilities in Internet Explorer and Twilio Authy to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog.
Organizations using these products are at increased risk of cyber attacks, making it crucial to address these vulnerabilities immediately to protect sensitive information and maintain security.
Recommendations
ATI recommends mitigative action occur according to the mitigation “Due Date” recommended by CISA.
Source Material: CISA
What We Mean When We Say
Estimates of Likelihood
We use probabilistic language to reflect the Intel Team’s estimates of the likelihood of developments or events because analytical judgments are not certain. Terms like “probably,” “likely,” “very likely,” and “almost certainly” denote a higher than even chance. The terms “unlikely” and “remote” imply that an event has a lower than even chance of occurring; they do not imply that it will not. Terms like “might” reflect situations where we are unable to assess the likelihood, usually due to a lack of relevant information, which is sketchy or fragmented. Terms like “we can’t dismiss,” “we can’t rule out,” and “we can’t discount” refer to an unlikely, improbable, or distant event with significant consequences.
Confidence in Assessments
Our assessments and projections are based on data that varies in scope, quality, and source. As a result, we assign our assessments high, moderate, or low levels of confidence, as follows:
High confidence indicates that our decisions are based on reliable information and/or that the nature of the problem allows us to make a sound decision. However, a “high confidence” judgment is not a fact or a guarantee, and it still carries the risk of being incorrect.
Moderate confidence denotes that the information is credible and plausible, but not of high enough quality or sufficiently corroborated to warrant a higher level of assurance.
Low confidence indicates that the information’s credibility and/or plausibility are in doubt, that the information is too fragmented or poorly corroborated to make solid analytic inferences, or that we have serious concerns or problems with the sources.

Share